Why Are Red Blood Cells Biconcave?
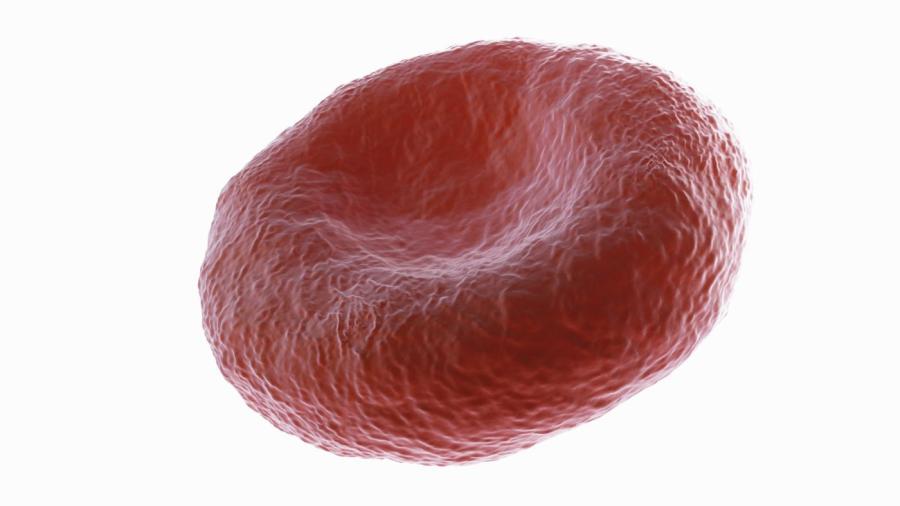
According to Santa Barbara City College, red blood cells’ biconcave shape gives them a vastly greater surface area than a spherical cell of similar volume, which allows them to absorb oxygen more efficiently. Red blood cells achieve this shape by losing their nucleus and many other organelles during development. Red blood cells can neither reproduce nor replenish cellular machinery, and they die off in large numbers over time.
Because of their inability to reproduce themselves, red blood cells, or erythrocytes, must be produced by stem cells, according to Santa Barbara City College. These stem cells are located in bone marrow and are relatively undifferentiated. Their only role is to reproduce cells with very different properties from themselves. The same stem cells in bone marrow form all the blood cells, including the white blood cells and platelets. They produce more red blood cells than any other type by far, however, and red blood cells are the most numerous single type of cell in the body at any one time. The stem cells create red blood cells in response to a hormone called erythropoetin, which is produced by the kidneys when they sense a drop in blood oxygen. Increased levels increase the oxygen levels in the blood, causing the kidneys to release less of the hormone.





