Where Is Nervous Tissue Found?
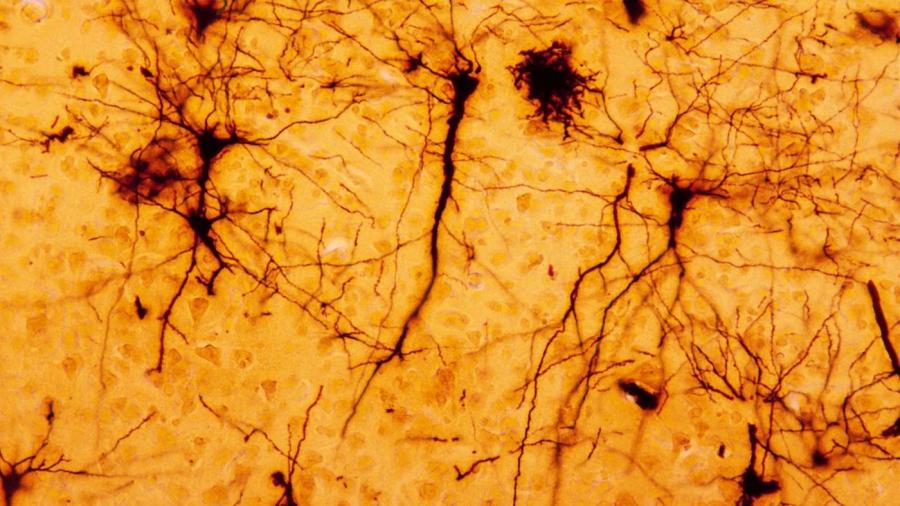
Nervous tissue is found in peripheral nerves throughout the body and in the organs of the central nervous system, the brain and spinal cord. Nerve tissue is composed of neurons, which are specialized cells able to react to stimuli by sending a signal down a long strand of cell known as an axon. Nervous tissue is responsible for receiving information from the senses, processing it and sending out instructions.
There are three types of nerves that compose nervous tissue, which vary by function, explains a University of Western Cape website. Sensory neurons, the neurons that receive information about touch and related senses, are also known as unipolar neurons. Their dendrites, which receive stimuli from the environment, and their axons, which transmit information about the stimuli, are on the same fiber. The cell body sits off to the side. Multipolar neurons have several branches of dendrites and one axon. Motor neurons, which transmit instructions to muscles, and interneurons, which act as intermediaries between other types of neurons, are both multipolar neurons. Bipolar neurons, such as those in the retina, have dendrites coming out one side and an axon out the other.
The connections between cells in nervous tissue are known as synapses. These are actually small gaps between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another, across which electrochemical signals are sent.





