What Is a Ventral Thecal Sac?
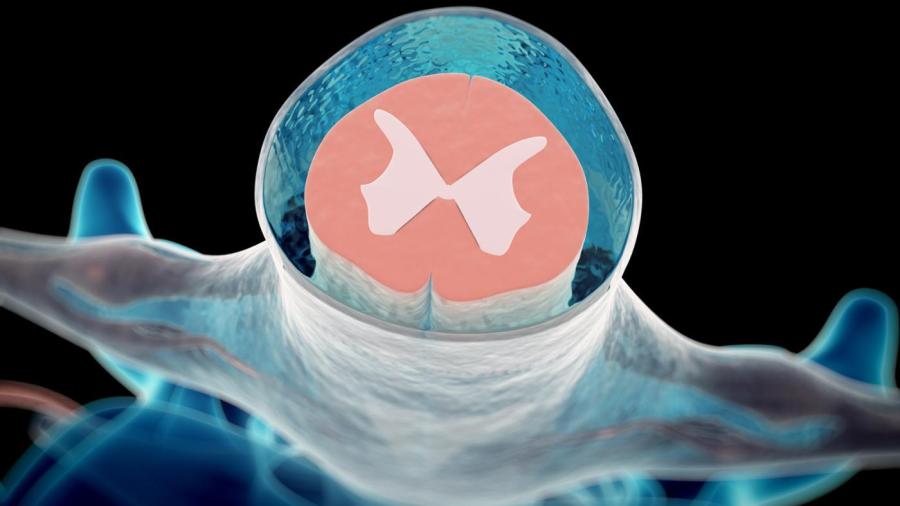
The ventral thecal sac refers to the ventral, or front side of the thecal sac, which is a membrane that surrounds the spinal cord and some cerebrospinal fluid. A diagnosis of spinal injury and disease takes the appearance of the thecal sac into consideration.
The thecal sac consists of dura mater, which is a thick membrane that surrounds and protects the brain. This membrane is the outermost of the three membranes that surround the brain, and it also encompasses the arachnoid mater and pia mater.
Ventral thecal sac indentation refers to parts of the vertebrae or spinal discs pressing on the front side of the thecal sac, causing indentations. Indentations into the thecal sac can result in pain or weakness as they pinch the nerves in the spinal cord.
Disc fragmentation in the spine can also affect the thecal sac. Although it is not common, if a disc ruptures, fragments may rupture the thecal sac.
Compression of nerve roots resulting in back pain can often be detected by looking at the thecal sac. The size of the thecal sac can help in determining the amount of cerebrospinal fluid. If there is not enough fluid inside, then the spinal cord is not properly protected by the thecal sac and is pinched.





