What Is the Function of the Nuclear Membrane?
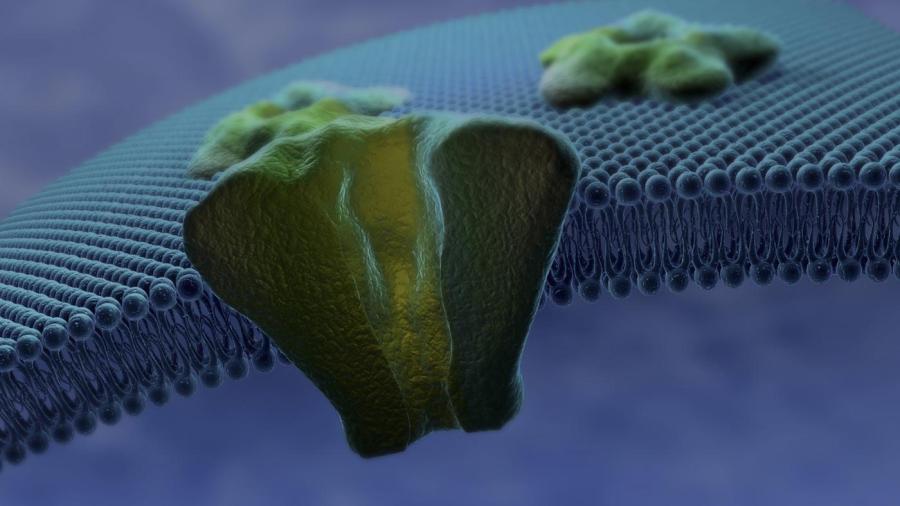
Defined by NCBI, the function of the nuclear membrane is to separate the nucleus of a cell from the cytoplasm that surrounds it. The nuclear membrane, also called the nuclear envelope, is defined as a membrane that surrounds the genetic material contained within the nucleus of a cell. The nuclear membrane is made up of the inner and outer membranes, the lamina and pore complexes.
The nuclear envelope is made up of phospholipids and surrounds the nucleus of a cell with a double-layered membrane comprised of multiple pores. These pores control how RNA and proteins pass through the membrane into the nucleus but allow water, ions and other small molecules to freely pass through.
The nuclear lamina is defined as lamin filaments that support the structure of the nucleus. The nuclear pore complexes are the only way molecules can move in and out of the cell nucleus. The pore complex is comprised of up to 100 different proteins and plays a large role in how proteins are synthesized within the cell.
Chromatin is contained within the nuclear envelope. Chromatin is DNA and protein that combined form chromosomes, which are the building blocks of cells and contain the genetic codes for cell replication.





