What Is the Function of the Cell Body?
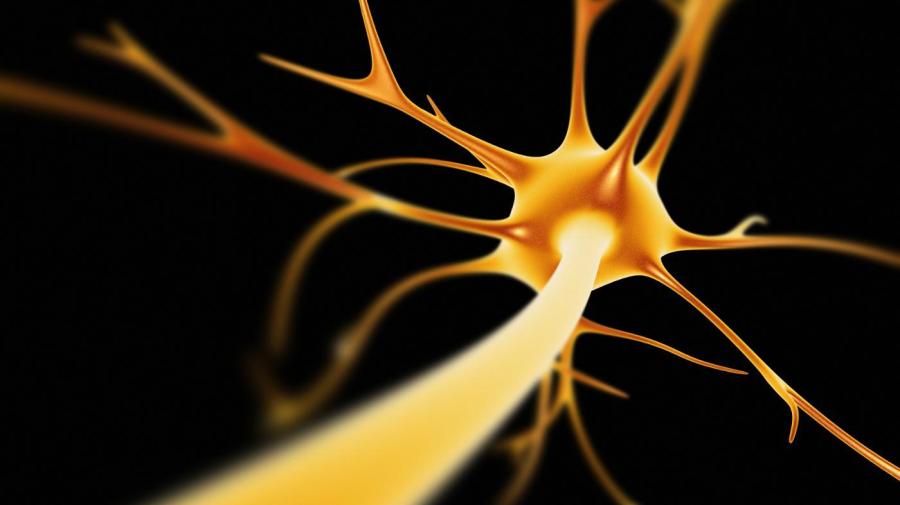
The main function of the cell body of a neuron is to integrate synaptic information and transmit this information to other cells via the axon. The cell body also completes a variety of biochemical processes to keep the neuron functioning properly.
Neurons are one of two cell types found in the nervous system. Their main function is to process and transmit information throughout the nervous system. Each neuron can be divided into three separate parts: the cell body, dendrites and the axon. The cell body is the portion of the neuron that contains the nucleus, the mitochondria, the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. Cell bodies also contain metabolic machinery to convert glucose into high-energy compounds such as ATP for the neuron to use as an energy source. Cell bodies also contain active proteins that act as chemical messengers throughout the neuron and the nervous system.
The organelles of the cell body carry out very distinct functions as well. The mitochondria supply the entire neuron with ATP and transport the ATP to the remaining parts of the neuron. The nucleus manufactures proteins and stores DNA molecules that code for all of the cells in the human body. The endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus work together to manufacture and process proteins. These organelles release proteins to the rest of the neuron that allow the neuron to function properly. Without the cell body, a neuron would not be able to function or transmit any signals.





