What Does Cytoplasm Do?
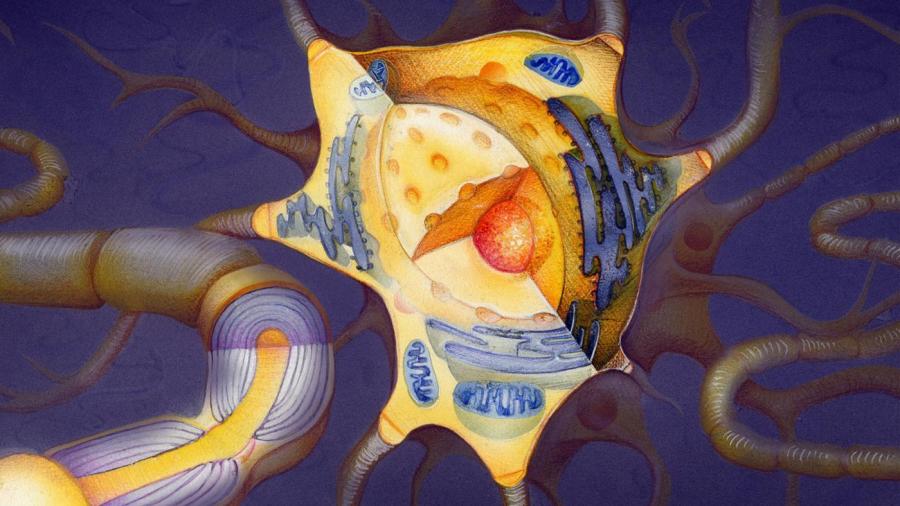
Cytoplasm is a clear, gel-like substance found in all cells. Everything contained within a cell is found suspended in cytoplasm, except the nucleus, which is separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane. Cytoplasm helps rid cells of waste material, aids in cell respiration and helps convert glucose into energy.
In a eukaryote cell, which is a cell that has a nucleus, mitochondria are found within the cytoplasm. All cell activity occurs within the cytoplasm, including cell division. In eukaryote cells, the mitochondria and other organelles are separated from other structures within the cell by a nuclear membrane. A prokaryote cell does not have a nucleus. Therefore, all structures within a prokaryote cell are found suspended in cytoplasm.
Cytoplasm is a colloid containing organic material, including lipids, carbohydrates, proteins and enzymes. Cytoplasm is 90 percent water and 10 percent inorganic and organic materials.
Cytoplasm transports material within a cell and plays a role in cell respiration. In a plant cell, cytoplasm provides the support and structure for the cell. Proteins are synthesized within the cytoplasm of a plant cell. In an animal cell, proteins, nucleotides and amino acids are present in the cytoplasm. Cytoskeleton is also present, aiding in the movement of the animal cell. Glycolysis, or the conversion of glucose to energy, occurs within the cytoplasm of a cell.





