What Is a Heart Echo Test?
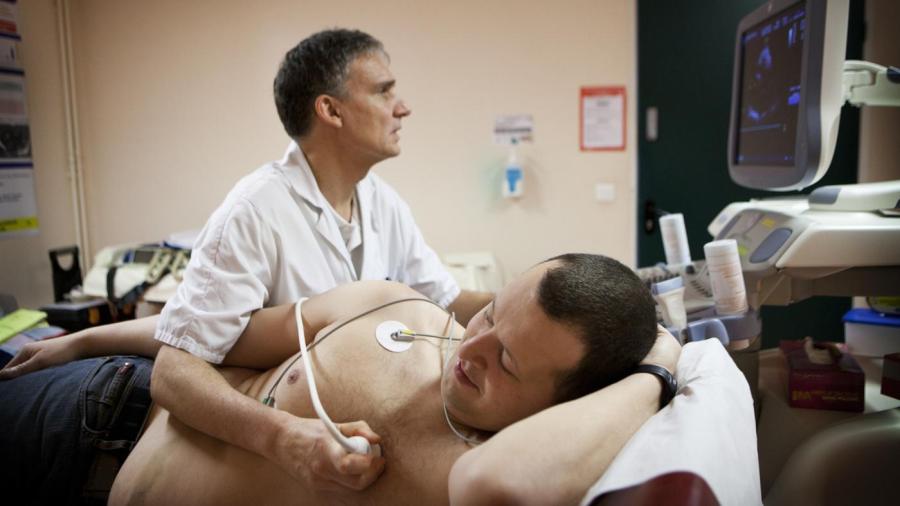
A heart echo test, or echocardiography exam, is a painless test that examines the structure and function of the heart, according to the National Institutes of Health. This test may involve the injection of saline or a specific dye into the patient’s veins to showcase his heart more easily.
Echocardiography tests utilize ultrasound technology to view a patient’s heart, states the National Institutes of Health. A doctor or a sonographer may apply lubricated gel to a patient’s chest and then place an ultrasound transducer onto his skin. The transducer is moved across the patient’s skin to view different angles of the heart.
Types of echocardiograms include transthoracic echocardiogram, stress echocardiogram, Doppler echocardiogram and transesophageal echocardiogram states WebMD. A transthoracic echocardiogram is performed to look for causes of abnormal heart sounds, an enlarged heart, chest pains, shortness of breath or irregular heartbeats. A stress echocardiogram is done to identify and monitor ischemia after a form of stress is induced. A Doppler echocardigram measures the blood pressure and speed of blood flow in the heart and heart valves. A transesophageal echocardiogram is done to monitor the heart during surgery.
When a doctor is interested in heart problems that occur during physical activity, Mayo Clinic indicates that he orders a stress test. During the stress test, the echocardiogram records the heart activity while the patient walks on a treadmill. For patients who have difficulty with exercise, the doctor injects a chemical into the bloodstream that increases the heart without exercise. These tests are especially useful in diagnosing coronary artery disease.





