What Happens If the Cerebral Cortex Is Damaged?
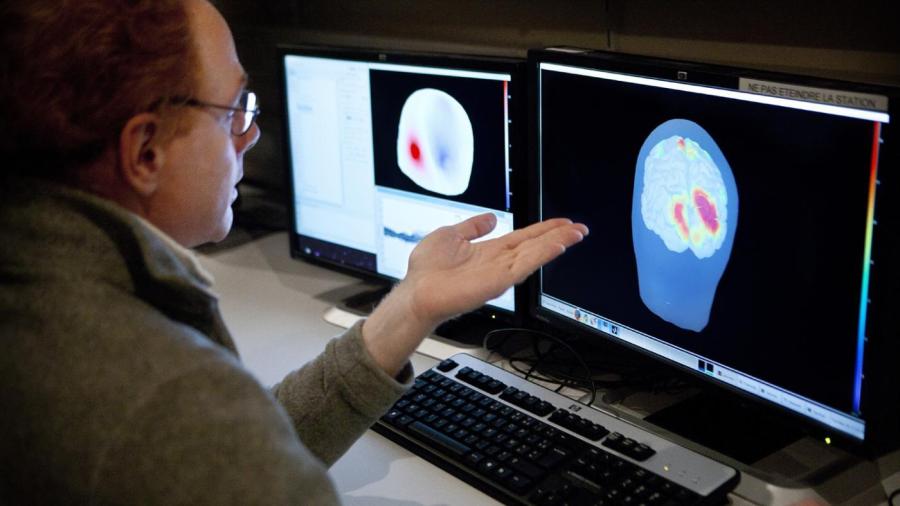
What happens when the cerebral cortex is damaged depends on the location of the damage, according to The University of Washington. As the largest part of the brain, the cerebral cortex is composed of the frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes. Damage to each of these lobes produces different symptoms.
According to the Centre for Neuro Skills, damage to the frontal lobe can cause loss of simple movement, decreased planning skills, mood and behavior changes and problems recalling the meanings of words. Damage to the parietal lobe can result in difficulty naming objects; trouble finding words when writing; difficulty reading, drawing and doing math; and problems with hand/eye coordination. Occipital lobe damage can result in vision problems, difficulty following moving objects, problems identifying colors and visual hallucinations. Damage in the temporal lobe may cause difficulty with facial recognition, problems understanding spoken words, trouble identifying and talking about objects and increased aggressiveness.
CT scans and MRIs can help locate the area of the cerebral cortex that has been damaged, the Centre for Neuro Skills states. This knowledge can help specialists identify which problems to watch for in someone with brain damage. Doctors may also learn more about the injury by watching the patient in daily life. The more a specialist knows about the injury and subsequent damage, the more accurately he is able to guide the patient through the rehabilitation process.





