What Are Causes for Myelocytes in Blood?
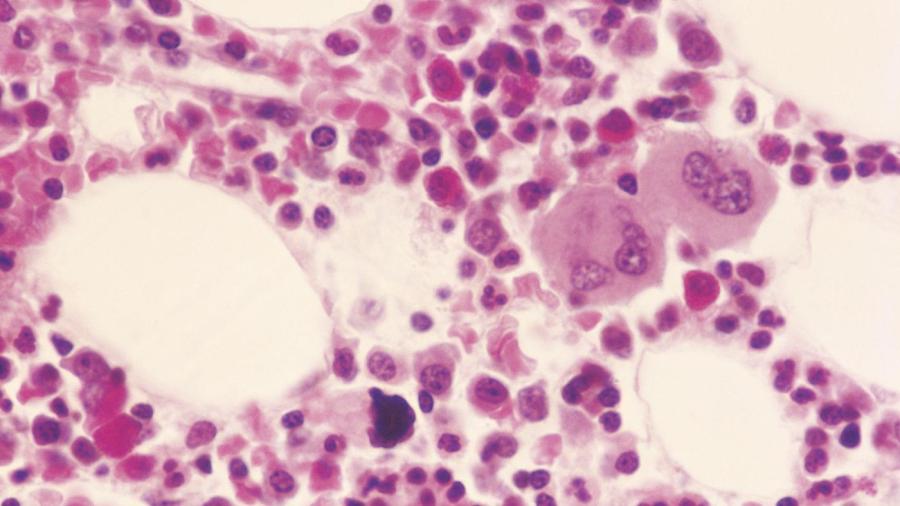
Leukemia can cause myelocytes in the blood. Cancereducation.com explains that blood containing an abnormally high number of white blood cells is often one of the first indications of leukemia. This occurs when the DNA in the person’s bone marrow mutates, and begins producing an abundance of myelocytes, which are abnormal, cancerous white blood cells. Doctors do not always understand why the bone marrow’s DNA changes, although exposure to radiation and organic solvents may be factors.
The primary job of white blood cells is to fight infection and pathogens. Cancereducation.com explains that most myelocytes turn into normal types of cells called basophils, neutrophils or eosinophils. However, when abnormal myelocytes are produced instead, they do not work properly. Georgetown University’s Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center explains that when this happens, the bone marrow becomes choked with abnormal cells; and, it cannot produce enough red blood cells and platelets to function properly. As a result, patients with leukemia bleed profusely when injured and experience chronic fatigue, as well.
Additionally, Georgetown University’s Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center explains that past treatment with some anti-cancer drugs can cause people to be at high risk for developing leukemia. Some common symptoms of leukemia include fevers of indeterminate origin, unexplained weight loss and chronic fatigue. Risk factors for leukemia include being male, advanced age and exposure to certain chemicals or radiation.





