Which Battery Is Equivalent to LR41?
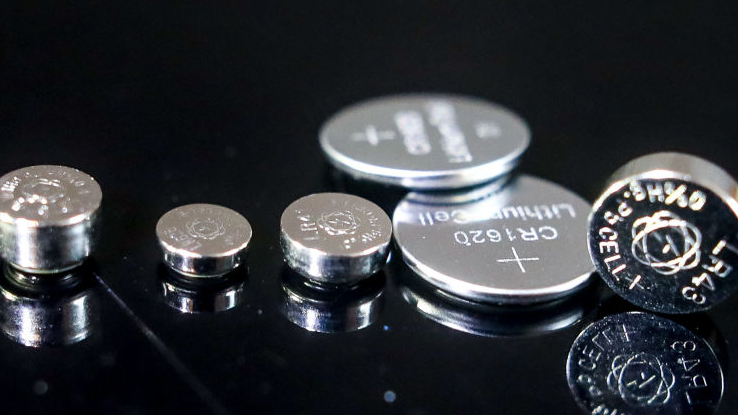

Because the LR41 battery is an AG3 battery equivalent, it can be safely replaced with 392, 392A, G3, V36, V36A, SR41, SR41SW, V3GA, 192, 384, 92A, GP192, LR736 and CX42 batteries. These batteries all have similar sizes and energy outputs, so which one you choose generally won’t matter. That said, silver oxide batteries, such as the SR41, tend to have more capacity than LR41 batteries, making them a great choice for powering electronics that consume more power. 384/392B batteries are one of the easiest equivalents to find in stores.
LR41 Batteries and Their Substitutes
Because LR41 batteries are so tiny, they’re often used to power watches, small medical devices, interactive cards and books, toys, laser pointers and more. They can be conveniently stacked on top of each other for more power and voltage. While the listed voltage of the battery is 1.5 volts, new LR41 batteries can have a charge as high as 1.62 volts.

To make them fit across many different electronic goods, all LR41 batteries and their equivalents have a diameter of 9.9 millimeters and a height of 3.6 millimeters (3.2 millimeters if you exclude the height of the button).
Alkaline Batteries
LR41 batteries are alkaline-based. That means they use zinc and manganese dioxide as electrodes and pass electrons through an alkaline solution — potassium or sodium hydroxide — to create power. Alkaline batteries are popular because they can store a large amount of energy for a fair amount of time. Because most such batteries don’t contain mercury, they are less damaging to the environment than some other kinds of batteries and can be disposed of at home without fear of leaking toxic chemicals. You can tell if a battery is mercury-free if it’s marked with the phrase “zero percent Hg.”

Alkaline batteries are very popular across the world. Most AAA, AA, C, D and 9V batteries sold in stores are alkaline-based, and those that aren’t are usually prominently labeled as such. Most alkaline batteries are primary batteries, meaning they’re used once and then tossed. Some alkaline batteries are secondary batteries, meaning they can be recharged, but you should never try to charge a battery that isn’t explicitly labeled as rechargeable. You also need to use the correct charger for any rechargeable batteries.
Silver Oxide Batteries
One popular substitute for LR41 batteries is the SR41 battery, which uses silver oxide along with zinc as its electrolytes. Potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide are used as the electrolyte in place of an alkaline solution. SR batteries are used for many of the same functions as LR41 batteries, including cash registers, watches, calculators, film cameras, microcomputers and other portable electronics that require a bit more energy than an alkaline battery can provide.
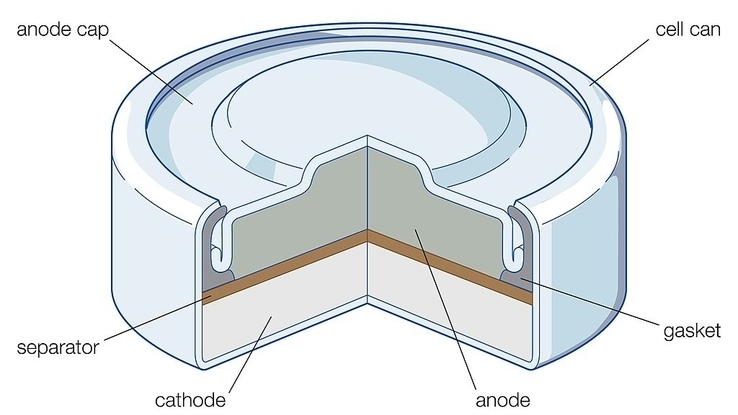
That’s because an SR battery can store almost twice as much energy as an alkaline battery. They provide a flat discharge, meaning release energy more evenly compared to alkaline batteries, which can shift more dramatically from releasing lots of energy at first to less and less as time goes on. That makes silver oxide batteries great for powering more delicate electronics that require a steadier flow of power. On top of that, they often have a shelf life of around ten years.
Other Batteries
There are other types of so-called button batteries in addition to alkaline and silver oxide, although they tend to see less usage. While mercury oxide batteries offer less voltage than alkaline batteries, they also come with greater capacity. Even so, the toxic nature of these batteries caused them to fall out of use.
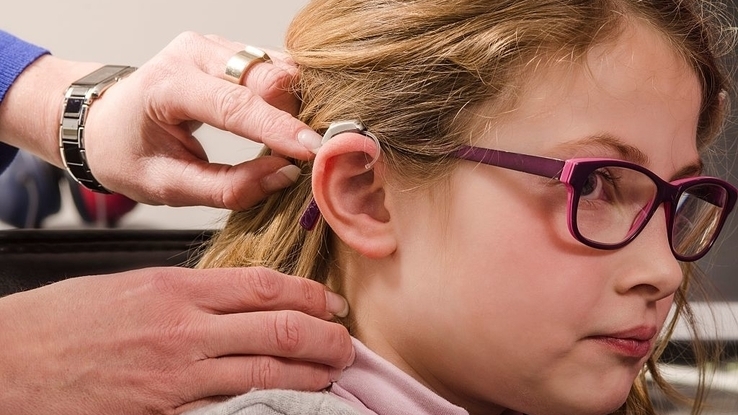
Zinc air batteries are unusual in that they harness the chemical reaction that happens when zinc is exposed to oxygen in the air, and they offer capacity even higher than silver oxide batteries with almost as much voltage as an alkaline battery. However, they become useless once their electrolyte dries out. They’re mostly used in hearing aids.





