Why Is the Egg Larger Than the Sperm?
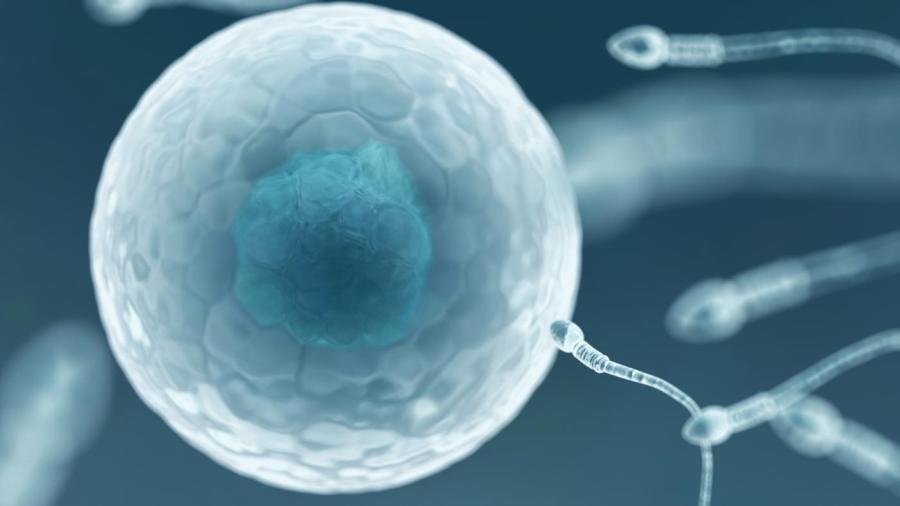
Egg cells are considerably larger than sperm cells because they carry the cytoplasm and organelles necessary for cell division and growth to begin, while sperm cells are basically a cell nucleus and a tail. Because the sole purpose of the sperm is to carry the father’s genetic information to the egg cell so fertilization can occur, small size and superior motility are advantageous.
An egg cell, or ovum, is the largest cell in the human body. It contains all of the organelles found in normal cells such as ribosomes, mitochondria, the golgi apparatus, the endoplasmic reticulum and a nucleus. It also contains several structures unique to the ovum such as the corona radiata and the zona pellucida. Some of these structures allow for fertilization by the sperm cell and others provide nourishment during the early stages of development. By contrast, the sperm cell is a simple structure. It consists of a small head containing a cell nucleus and a long whip-like tail. There is also a tube-shaped section connecting the head to the tail. This section houses the mitochondria that provide the energy for the tail to move. If fertilization occurs, the nucleus of the sperm enters the ovum and the two half-sets of chromosomes merge to form a complete set. The fertilized ova is called a zygote, and it contains all the elements necessary to develop into an embryo.





